Benchmarking
When you use the Hasura GraphQL Engine with YugabyteDB, you have an option to use a benchmark tool created by Yugabyte.
For information on Hasura, see the following:
- Hasura GraphQL Engine documentation
- Scaling GraphQL Subscriptions to One Million Subscribers Linearly
- High Availability of GraphQL Subscriptions Under Infrastructure Failures
Prerequisites
Before using Hasura with YugabyteDB, perform the following:
- Install and start YugabyteDB, as described in Quick Start Guide.
- Familiarize yourself with information on how to install and start Hasura on an existing database by reading Run Hasura GraphQL Engine on Kubernetes.
To use Hasura with YugabyteDB, the configuration should be similar to PostgreSQL, except that the port should be 5433.
Set up the benchmark
You can use a benchmark tool to deploy the benchmark setup on a Kubernetes cluster. The entire setup runs inside Kubernetes and includes the following components:
- A YugabyteDB cluster running natively inside Kubernetes.
- A Hasura Kubernetes service.
- A sample application consisting of a load generator that produces user orders and a GraphQL application that subscribes to incoming orders.
The following diagram illustrates the setup:
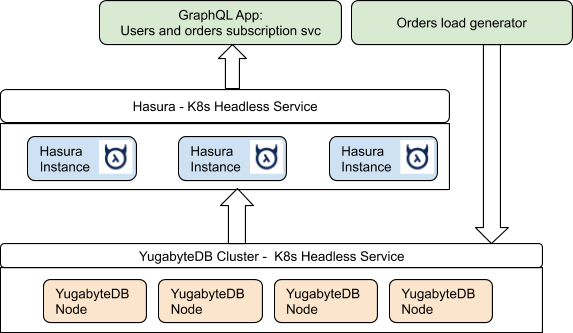
Sample application
The sample application provides a simulation of users placing orders that require delivery. Each order is tracked and a notification is posted in real time to trigger the order fulfillment.
The following user_account table contains information about the user:
CREATE TABLE user_account (
userID BIGINT NOT NULL,
accountName VARCHAR,
givenName VARCHAR,
middleName VARCHAR,
familyName VARCHAR,
userGender VARCHAR,
userAge INT,
dob TIMESTAMP,
address1 VARCHAR,
address2 VARCHAR,
city VARCHAR,
zip VARCHAR,
email VARCHAR,
homePhone VARCHAR,
mobilePhone VARCHAR,
country VARCHAR,
company VARCHAR,
companyEmail VARCHAR,
active BOOLEAN,
PRIMARY KEY (userID HASH)
);
CREATE INDEX user_fname ON user_account (givenName) ;
CREATE INDEX user_lname ON user_account (familyName) ;
The following user_orders table contains a list of orders placed by the user:
CREATE TABLE user_orders (
userID BIGINT NOT NULL ,
orderID VARCHAR NOT NULL ,
orderTotal VARCHAR NOT NULL ,
orderDetails VARCHAR NOT NULL,
orderTime TIMESTAMP NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (userID HASH, orderID ASC)
);
ALTER TABLE user_orders ADD FOREIGN KEY (userID) REFERENCES user_account(userID);
The following events table is used for verifying that all subscriptions are received by the GraphQL tool:
CREATE TABLE events (
label VARCHAR NOT NULL,
connection_id INT NOT NULL,
operation_id INT NOT NULL,
event_number INT NOT NULL,
event_data JSONB NOT NULL,
event_time TIMESTAMP NOT NULL,
is_error BOOLEAN NOT NULL,
latency INT,
PRIMARY KEY (connection_id HASH, label, operation_id, event_number)
);
The following is the dominant query performed using subscriptions in Hasura. This query produces a list of the most recent orders placed by a given user:
subscription ($id: bigint!) {
user_account (where: {userid: {_eq: $id}}) {
accountname
givenname
familyname
city
user_orders(order_by: {orderid: desc}) {
orderid
ordertotal
orderdetails
ordertime
}
}
}
Deploy the benchmark setup
Deploying the benchmark setup is a multi-step process that involves deployment of a YugabyteYB cluster using Helm charts on Kubernetes, preparing the database with table schema, deployment of Hasura, loading of tables, deployment of GraphQL subscription performance tool, and starting table data load.
Deploy a YugabyteYB cluster
-
Follow instructions provided in Deploy on Kubernetes to deploy a YugabyteYB cluster using Helm charts on Kubernetes.
-
Ensure that your YugabyteDB cluster resources are 3 pods x 16 vCPU, 32GB RAM, and 2 x 100 GB SSD.
-
Execute the following command to obtain the information about
external-IPforyb-tserver-servicethat are required for establishing a connection between YugabyteDB and the serverless application:$ kubectl get services --namespace yb-demoThe following illustration shows the output of the preceding command:

Prepare the database with table schema
-
Open
ysqlsh, specify the Yugabyte user, and trigger the password prompt by executing the following command:$ ./ysqlsh -U yugabyte -W -
When prompted for password, enter the Yugabyte password (the default password is yugabyte). Expect the following output:
ysqlsh (11.2-YB-2.23.1.0-b0) Type "help" for help. yugabyte=# -
Create a database called
hasuratestby executing the following command:yugabyte=# create database hasuratest; -
Create the database tables by executing the following commands:
./bin/ysqlsh -h <yb-tserver-service> -f ./resources/user.sql ./bin/ysqlsh -h <yb-tserver-service> -f ./resources/user_orders.sql ./bin/ysqlsh -h <yb-tserver-service> -f ./resources/events.sql
Deploy Hasura
-
Deploy one Hasura pod with resource definition of 4 vCPU, 8GB RAM (20k subscriptions per Hasura instance) by executing the following command:
kubectl apply -f ./resources/deployment.yaml kubectl apply -f ./resources/svc.yaml -
Track tables and relationships from Hasura console.
-
Update the stateful set to deploy five Hasura instances (100K subscriptions in total).
Load the primary table and users table
Load one million users into the user_account table by using yb-sample-apps data loader, as follows:
kubectl run --image=nchandrappa/yb-sample-apps:1.0.12-SNAPSHOT yb-sample-apps-01 --limits="cpu=3200m,memory=4Gi" --requests="cpu=3000m,memory=4Gi" -- --workload SqlProductUserOrdersUpdate --nodes yb-tserver-0.yb-tservers.yb-dev-hasura-perf-cluster.svc.cluster.local:5433 --num_unique_keys 1000000 --num_threads_read 0 --num_threads_write 10 --batch_size 5 --data_load_prefix 0 --action_type loadprimary --default_postgres_database hasuratest --num_writes 1000000
Deploy the GraphQL Subscriptions Performance tool
There is a procedure that simulates acquiring 100,000 subscribers using the GraphQL subscription performance tool.
-
Use the following subscription query:
apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: graphql-perf-tool-config namespace: default data: config.yaml: | query: | subscription ($id: bigint!) { user_account (where: {userid: {_eq: $id}}) { accountname givenname familyname city user_orders(order_by: {orderid: desc}, limit: 2) { orderid ordertotal orderdetails ordertime } } } timePeriod: 1000 statsCountInsertInterval: 100 variables: id: '1' headers: content-type: 'application/json' template: range: start: 1 end: 25000 headers: content-type: 'application/json' variables: - id -
Execute the following command to configure the subscription query to be benchmarked with the subscription performance tool:
kubectl apply -f configmap.yaml -
Apply the following properties to the subscription performance tool:
perf.config.file.path=/app/config.yaml perf.config.db.connection=postgres://yugabyte@yb-tserver-2.yb-tservers.yb-dev-hasura-perf-cluster.svc.cluster.local:5433/hasuratest perf.config.graphql.endpoint=ws://hasura-0.hasura-headless.default.svc.cluster.local:8080/v1/graphql -
The preceding configuration enables the subscription performance tool to connect to YugabyteDB cluster and Hasura GraphQL Engine. To create connection, execute the following command:
kubectl create configmap graphql-perf-properties --from-env-file env.properties -
Deploy the subscription performance tool on Kubernetes by executing the following command:
kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml
Load data into a table
Execute the following command to trigger loading of data into the orders table for simulating the new order being placed in the system:
kubectl run --image=nchandrappa/yb-sample-apps:1.0.12-SNAPSHOT yb-sample-apps-01 --limits="cpu=4200m,memory=4Gi" --requests="cpu=3800m,memory=4Gi" -- --workload SqlProductUserOrdersUpdate --nodes yb-tserver-0.yb-tservers.yb-dev-hasura-perf-cluster.svc.cluster.local:5433 --num_unique_keys 100000 --num_threads_read 0 --num_threads_write 2 --batch_size 4 --data_load_prefix 0 --action_type loadforeign --default_postgres_database hasuratest --num_writes 1000000