Set up xCluster Replication
Prerequisites
To set up or configure xCluster replication, you must be a Super Admin or Admin, or have a role with the Manage xCluster permission. For information on roles, refer to Manage users.
Create the source and target universes for replication.
Ensure the universes have the following characteristics:
-
Both universes are running the same version of YugabyteDB (v2.18.0.0 or later).
-
Both universes have node-to-node encryption enabled (recommended) or both have this setting disabled.
-
They can be backed up and restored using the same storage configuration.
The storage configuration for copying data from source to target must be accessible from both universes. For example, if AWS S3 is used as the target of backups, the same S3 bucket must be accessible from the source and target universe.
If an NFS file server is used, the file server or a mirror of the file server in the target region must be accessible at the same mount point on both universes. If there is significant delay in file transfer between the file server and its mirror in a different region, set the runtime configuration
yb.xcluster.sleep_time_before_restoreto the maximum delay in mirroring files across the regions. -
They have enough disk space to support storage of write-ahead logs (WALs) in case of a network partition or a temporary outage of the target universe. During these cases, WALs will continue to write until replication is restored. Consider sizing your disk according to your ability to respond and recover from network or other infrastructure outages.
In addition, during xCluster Replication setup, the source universe retains WAL logs and increases in size. The setup (including copying data from source to target) is not aborted if the source universe runs out of space. Instead, a warning is displayed notifying that the source universe has less than 100 GB of space remaining. Ensure that there is enough space available on the source universe before attempting to set up the replication.
-
They have network connectivity; see Networking for xCluster. If the source and target universe Master and TServer nodes use DNS addresses, those addresses must be resolvable on all nodes.
Best practices
-
Monitor CPU use and keep it at 65% or less.
-
Monitor disk space and keep its use under 65%.
-
Set the YB-TServer log_min_seconds_to_retain flag to 86400 on both source and target.
This flag determines the duration for which WAL is retained on the source in case of a network partition or a complete outage of the target. For xCluster Replication, you should set the flag to a value greater than the default. The goal is to retain write-ahead logs (WALs) during a network partition or target outage until replication can be restarted. Setting this to 86400 (24 hours) is a good rule of thumb, but you should also consider how quickly you will be able to recover from a network partition or target outage.
In addition, during an outage, you will need enough disk space to retain the WALs, so determine the data change rate for your workload, and size your disk accordingly.
-
Set a replication lag alert for the source to be alerted when the replication lag exceeds acceptable levels.
-
Add new tables and databases to the replication configuration soon after creating them, and before performing any writes to avoid the overhead of a full copy.
-
If xCluster Replication setup clashes with scheduled backups, wait for the scheduled backup to finish, and then restart the replication.
Configure replication
Prepare your database and tables on the source. The source can be empty or have data.
During initial setup, or when adding a database, you don't need to create objects on the target. YugabyteDB Anywhere performs a full copy of the data to be replicated on the source, and automatically creates tables and objects, and restores data on the target from the source.
If the source has a lot of data, setup will take longer because the data must be copied in full to the target before on-going asynchronous replication starts.
Set up xCluster Replication
To set up replication for a universe, do the following:
-
Navigate to your source universe and select xCluster Replication.
-
Click Configure Replication.
-
Enter a name for the replication.
-
Select the universe to use as the target.
-
Select the table type, YSQL or YCQL.
-
If you selected YSQL, choose whether to use transactional atomicity.
-
Click Next: Select Databases (YSQL) or Select Tables (YCQL).
-
Select the databases or tables to be copied to the target for replication.
For YSQL, select the database(s) with the tables you want in replication. All tables in a selected database are added. Colocated tables require additional conditions. For more information, see YSQL tables.
For YCQL, you can select individual tables.
-
Click Validate Table Selection.
YugabyteDB Anywhere checks whether or not data needs to be copied to the target for the selected databases and its tables. See Full copy during xCluster setup.
-
If data needs to be copied, click Next: Configure Full Copy, and select a storage configuration.
The storage is used to transfer the data to the target database. For information on how to configure storage, see Configure backup storage.
-
Click Next: Confirm Alert Threshold.
If you have set an alert for replication lag on the universe, the threshold for alerting is displayed.
-
Click Confirm and Enable Replication.
YugabyteDB Anywhere proceeds to set up replication for the universe. How long this takes depends mainly on the amount of data that needs to be copied to the target. You can view the progress of xCluster tasks by navigating to the universe Tasks tab.
Add a database to an existing replication
For information on adding a database to bidirectional replication, see Add a database to bidirectional replication.
To add a database to replication, do the following:
-
Navigate to the source universe xCluster Replication tab and select the replication configuration.
-
Click Actions > Select Databases and Tables.
-
Select the databases to be copied to the target for replication.
All tables in a selected database are added. Colocated tables require additional conditions. For more information, see YSQL tables.
-
Click Validate Selection.
YugabyteDB Anywhere checks whether or not data needs to be copied to the target for the selected databases and its tables. See Full copy during xCluster setup.
-
If data needs to be copied, click Next: Confirm Full Copy.
-
Click Apply Changes.
YugabyteDB Anywhere proceeds to copy the database to the target. How long this takes depends mainly on the amount of data that needs to be copied.
Full copy during xCluster setup
When xCluster is set up or restarted, or when new tables or databases are added to an existing xCluster configuration, YugabyteDB Anywhere checks if a full copy is required before configuring the replication.
A full copy is required in the following circumstances:
- Any databases or tables or index tables being added are not empty. Newly created index tables associated with non-empty main tables are considered non-empty and trigger a full copy.
- Any newly added databases or tables or index tables are not present on the target universe.
For YSQL, the entire database is copied; for YCQL, the table (including associated index tables) is copied.
Ideally, you should add tables to replication right after creating them on both universes to avoid unnecessary full copy operations.
A full copy is done by first backing up the data to external storage, and then restoring to the target universe.
- For information on creating and using storage configurations, refer to Configure backup storage.
- To configure the performance of backup and restore, refer to Configure backup performance parameters.
YSQL tables
You can add databases containing colocated tables to the xCluster configuration as long as the underlying database is v2.18.1.0 or later. Colocated tables on the source and target should be created with the same colocation ID if they already exist on both the source and target prior to setup. Refer to xCluster and colocation.
If a full copy is required, the entire database is recreated on the target universe from the current database on the source universe. Be sure to keep the set of tables the same at all times on both the source and target universes in these databases by following the steps in Manage tables and indexes.
Monitoring and alerts
After replication is set up, the xCluster Replication tab displays the status.
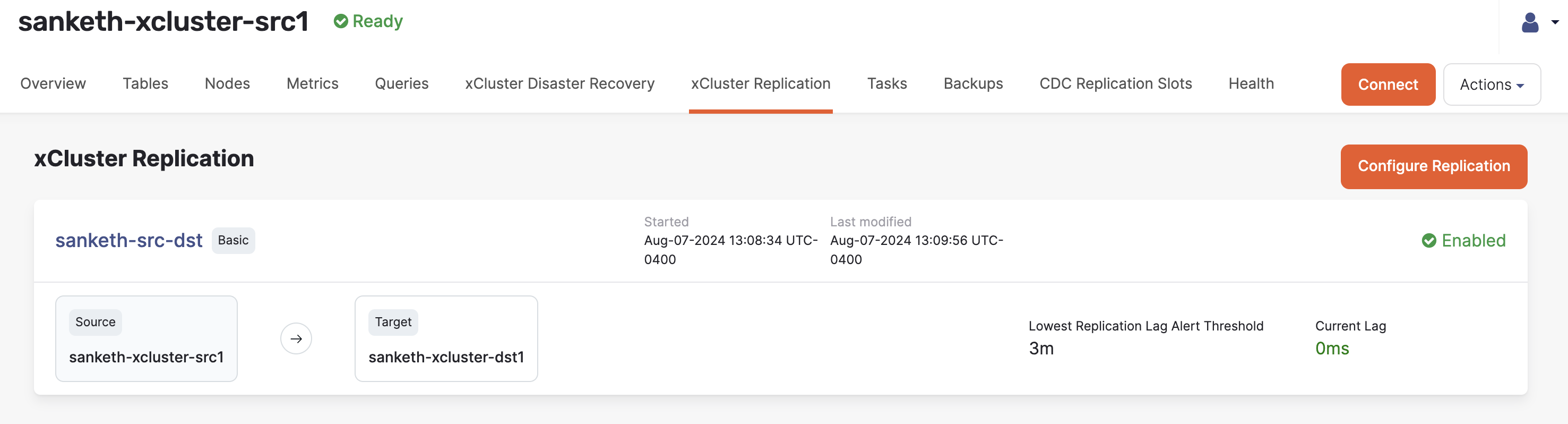
To display the replication details, click the replication name.
Metrics
You can monitor the following metrics on the Metrics tab:
-
Async Replication Lag
The network lag in microseconds between any two communicating nodes.
If you have set an alert for replication lag, you can also display the alert threshold.
YSQL transactional replication displays the following additional metrics:
-
Consumer Safe Time Lag
The time elapsed in microseconds between the physical time and safe time. Safe time is the time (usually in the past) at which the database or tables can be read with full correctness and consistency. For example, even though the actual time may be 3:00:00, a query or read against the target database may be able to only return a result as of 2:59:59 (that is 1 second ago) due to network lag and/or out-of-order delivery of datagrams.
-
Consumer Safe Time Skew
The time elapsed in microseconds for replication between the most caught up tablet and the tablet that lags the most on the target. This metric is available only on the target.
For more information, refer to Metrics.
Tables
The replication details also provide all the tables in replication and their status on the Tables tab.
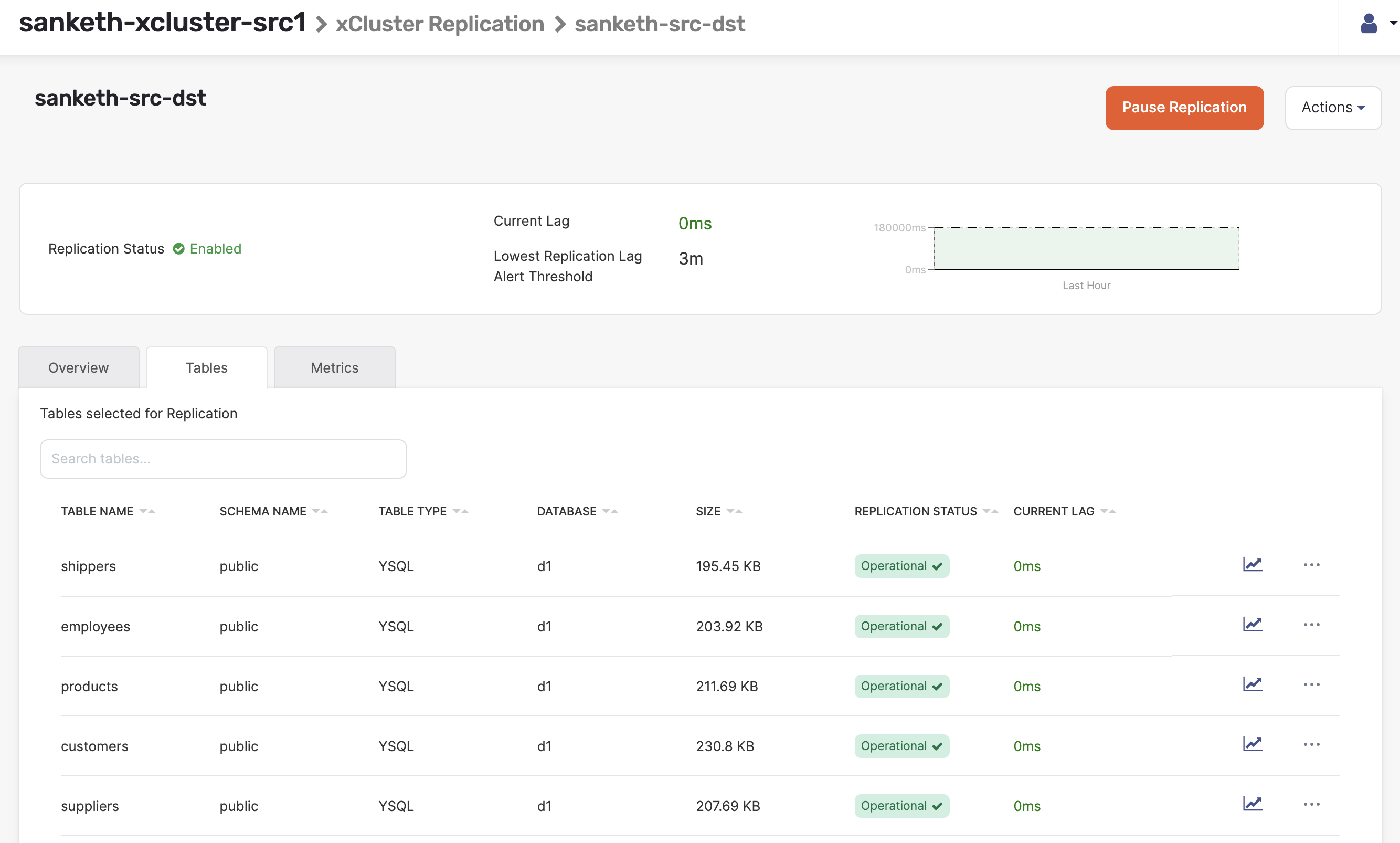
-
To find out the replication lag for a specific table, click the graph icon corresponding to that table.
-
To check if the replication has been properly configured for a table, check the status. If properly configured, the table's replication status is shown as Operational.
The status will be Not Reported momentarily after the replication configuration is created until metrics are available for the replication configuration. This should take about 10 seconds.
If the replication lag increases beyond maximum acceptable lag defined during the replication setup or the lag is not being reported, the table's status is shown as Warning.
If the replication lag has increased so much that resuming or continuing replication cannot be accomplished via WAL logs but instead requires making another full copy from source to target, the status is shown as Error: the table's replication stream is broken, and restarting the replication is required for those tables. If a lag alert is enabled on the replication, you are notified when the lag is behind the specified limit, in which case you may open the table on the replication view to check if any of these tables have their replication status as Error.
If YugabyteDB Anywhere is unable to obtain the status (for example, due to a heavy workload being run on the universe) the status for that table will be UnableToFetch. You may refresh the page to retry gathering information.
-
To delete a table from the replication, click ... > Remove Table. This removes both the table and its index tables from replication. If you decide to remove an index table from the replication group, it does not remove its main table from the replication group.
Set up replication lag alerts
Replication lag measures how far behind in time the target lags the source. In a failover scenario, the longer the lag, the more data is at risk of being lost.
To be notified if the lag exceeds a specific threshold so that you can take remedial measures, set a Universe alert for Replication Lag. Note that to display the lag threshold in the Async Replication Lag chart, the alert Severity and Condition must be Severe and Greater Than respectively.
To create an alert:
-
Navigate to Admin > Alert Configurations > Alert Policies.
-
Click Create Alert Policy and choose Universe Alert.
-
Set Policy Template to Replication Lag.
-
Enter a name and description for the alert policy.
-
Set Target to Selected Universes and select the source.
-
Set the conditions for the alert.
- Enter a duration threshold. The alert is triggered when the lag exceeds the threshold for the specified duration.
- Set the Severity option to Severe.
- Set the Condition option to Greater Than.
- Set the threshold to an acceptable value for your deployment. The default threshold is 3 minutes (180000ms).
-
Click Save when you are done.
When replication is set up, YugabyteDB automatically creates the alert XCluster Config Tables are in bad state. This alert fires when:
- there is a table schema mismatch between DR primary and replica
- tables are added or dropped from either DR primary or replica, but have not been added or dropped from the other.
When you receive an alert, navigate to the replication configuration Tables tab to see the table status.
YugabyteDB Anywhere collects these metrics every 2 minutes, and fires the alert within 10 minutes of the error.
For more information on alerting in YugabyteDB Anywhere, refer to Alerts.
Manage replication
Restart replication
Some situations, such as extended network partitions between the source and target, can cause a permanent failure of replication due to WAL logs being no longer available on the source. For information on restarting bidirectional replication, see Restart bidirectional replication.
In these cases, restart replication as follows:
-
Navigate to the universe xCluster Replication tab and select the replication configuration.
-
Click Actions and choose Restart Replication.
-
Select the databases to be copied to the target.
-
Click Next: Configure Full Copy and choose the storage configuration.
-
Click Create a New Full Copy.
This performs a full copy of the databases (YSQL) or tables (YCQL) involved from the source to the target.
Pause and remove replication
To pause xCluster Replication for a universe, do the following:
-
Navigate to the universe xCluster Replication tab and select the replication configuration.
-
Click Pause Replication.
To remove xCluster Replication for a universe, do the following:
-
Navigate to the universe xCluster Replication tab and select the replication configuration.
-
Click Actions and choose Delete Replication.
You can opt to ignore errors and force delete the replication, but this is not recommended except in some rare scenarios. You can use this option to delete the xCluster configuration when one of the universes is inaccessible. However, doing so may cause some state information related to replication to be left behind on the underlying YugabyteDB universes that will require manual cleanup later on.
Upgrading the database version
Use the same version of YugabyteDB on both the source and target.
When upgrading universes in xCluster Replication, you should upgrade and finalize the target universe before upgrading and finalizing the source universe.
If you upgrade and finalize the source universe first, replication may be paused automatically until both universes are finalized to the same software version.
Rotating CA certificates
If you rotate the CA certificate on the source universe, you need to restart the replication so that the target nodes get the new root certificate for TLS verifications.